Vespa affinis (Linnaeus, 1764)Lesser banded hornet
Table of Contents
 |
(1) OVERVIEW
When asked about bees, wasps or hornet, the first thing that comes to mind is either the honey bees that live in hives and produce honey or the perceived danger posed by these insects where they should be removed from human dwellings. Despite exploiting bees worldwide to produce many products for humans such as honey, beeswax and royal jelly, many lack the knowledge to differentiate these insects. Although some species are indeed dangerous when provoked, people need to better understand and gain greater appreciation of these insects, for over 100 known species of bees have been found in Singapore (Ascher, personal communication, 2015).
No doubt, bees and wasps are one of the most venomous insect groups (4). One group is the genus Vespa, which composes 22 extant species of hornet. A hornet is a type of social wasp in the genus Vespa. You will learn later that these social wasps possess a social organization system that is orderly yet complex. Several hornet species have been extensively studied for their social habits and threats to human. One species is the lesser banded hornet (Vespa affinis), which is one of the three common species found in Singapore. Before that, let's learn how to differentiate bees and wasps.
1.1 Differentiating bees and wasps
Without close examination, bees and wasps can be easily confused in the field even by trained taxonomists. It is important to distinguish these insects so that control methods can be effectively employed (5).Bee Figure 1. Apis cerana (Photo by John S. Ascher) |
Solitary Wasp Figure 2. Solitary wasps(Photo by John X. Q. Lee) |
Social Wasp Figure 3. Vespa affinis (Photo by John X. Q. Lee) |
|
| Morphology |
Hairs on bodies Specialization of hindleg |
Little hairs on bodies Simple, unmodified legs Narrower waist than bee |
No hairs on bodies Simple, unmodified legs Narrower waist than bee More robust than solitary wasp |
| Nest |
Generally live in hives |
Build nests in all places such as hollow trees,existing crevices and cavities Rarely live in their nests Nests are for prey storage and incubation of offspring |
Live in nests, hollow trees |
| Food |
Nectar and pollen |
Nectar and pollenInsects |
Nectar and pollenInsects |
| Sting habits |
Honeybees sting once only Solitary bees may sting repeatedly |
Sting repeatedly |
Sting repeatedly |
1.2 Facts on Lesser banded hornet
- Lesser banded hornet is very diverse – There are 11 known subspecies across Asia, each with different colour variations (1)
- They are highly eusocial – There is a reproductive division of labour, comprising of a queen, male drones and female workers. Within this caste system, the queen and male drones engage in reproduction while the sterile female workers engage in task such as foraging (3) (Section 5.1 & 5.2)
- They can sting repeatedly – Like most bees and wasps, only females have unbarbed sting (4)
- They have venomous stings – Fatal stinging cases have been reported across Southeast Asia (4)
- They are considered as pests, especially when they nest near human dwellings (4)
- They are biological pest control that feed on insects (Fig. 5)
 |
 |
| Figure 4. Nest of Vespa affinis(Photo by John S. Ascher) |
Figure 5. Vespa affinis feeding on an insect(Permission pending from Nikita Hengbok) |
1.3 Other species of hornets found in Singapore
Besides the lesser banded hornet, Singapore is home to two other species, namely, the greater banded hornet (Vespa tropica) and the yellow-vented hornet (Vespa analis). These hornets are native to the tropical regions, distributing across Southeast Asia. These species can be easily distinguished by the size, clypeus proportions and distribution of yellow-orange band on the abdomen (2).
| Vespa affinis Lesser banded hornet |
Vespa tropica Greater banded hornet |
Vespa analis Yellow-vented hornet |
|
| Size / Body length |
Queens: ~30mm Workers and male: 20mm – 27mm |
Queens: ~35mm Workers and male: 23mm – 30mm |
Queens: Not recorded Workers and male: ~25mm |
| Clypeus proportions (Permission pending: Gopalakrishnakone) |
 Figure 6. Width of clypeus longer than its height |
 Figure 7. Width of clypeus shorter or sub-equal to its width |
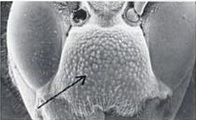 Figure 8. Narrow rounded lobes |
| Distribution of yellow-orange band on the abdomen |
 Figure 9. 1st and 2nd segment yellow (Photo by Troup Dresser) |
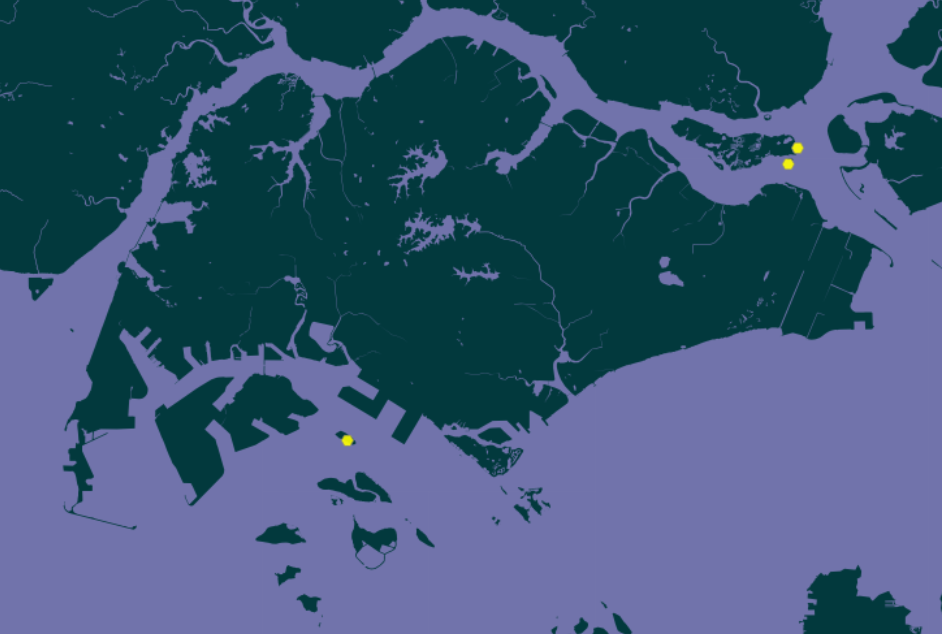 Figure 10. 2nd segment yellow (Photo by John X. Q. Lee) |
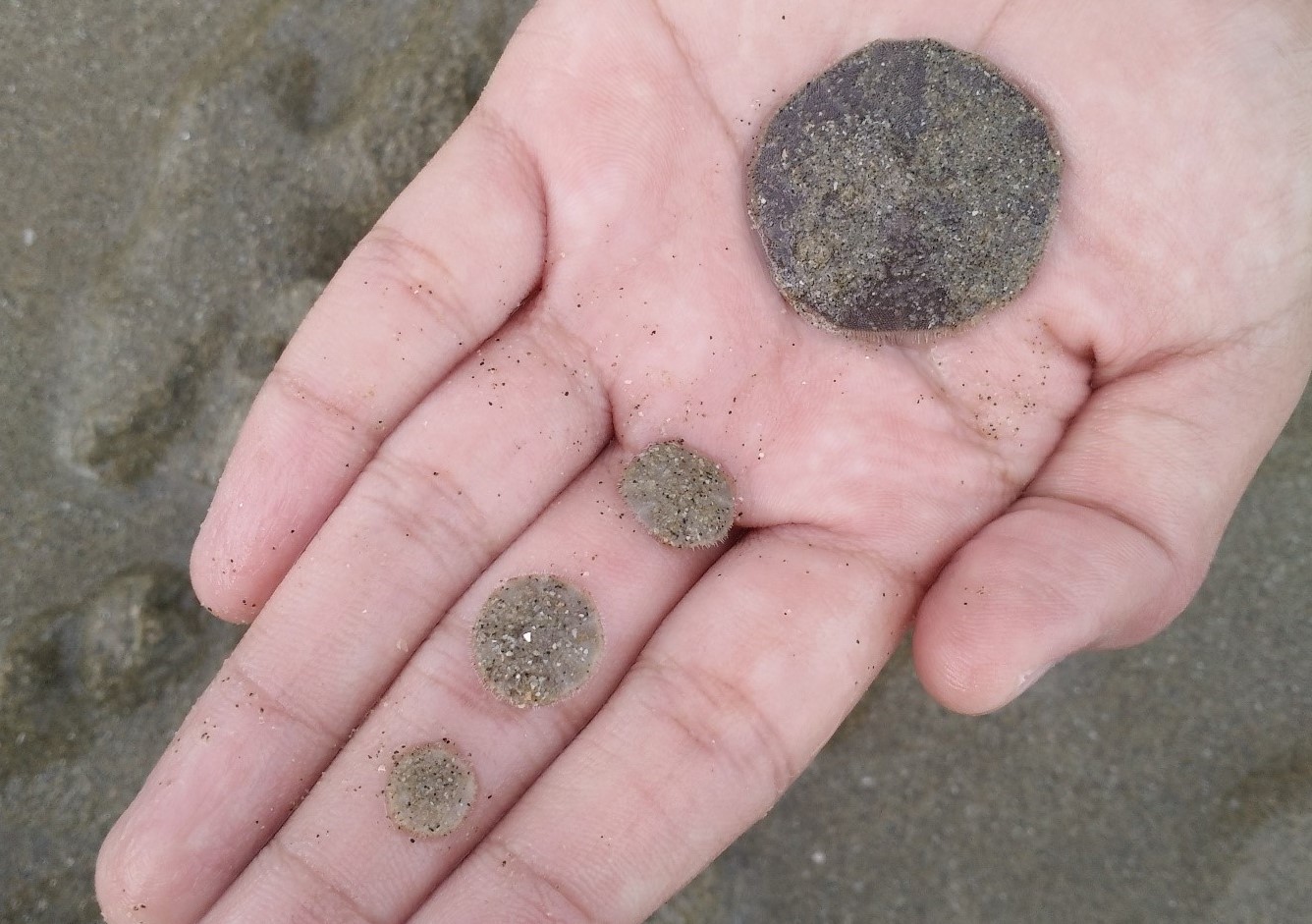 Figure 11. Last segment yellow (Photo by Kwan Han) |
(2) DISTRIBUTION
2.1 Habitat
Lesser banded hornet occurs mainly in lowlands of tropical and sub-tropical regions of Asia (9). They nest above ground on a variety of supports such as trees, bushes, shrubs and even buildings (6). As such, they seem to have adjusted to the urbanization in Singapore where they have been found foraging in urban gardens, parks and rooftop gardens (observation, 2015). Although they are more commonly found close to the ground in grassy areas, forest or wasteland, their preference for natural or man-made habitats have yet to be discovered.
2.2 Global distribution
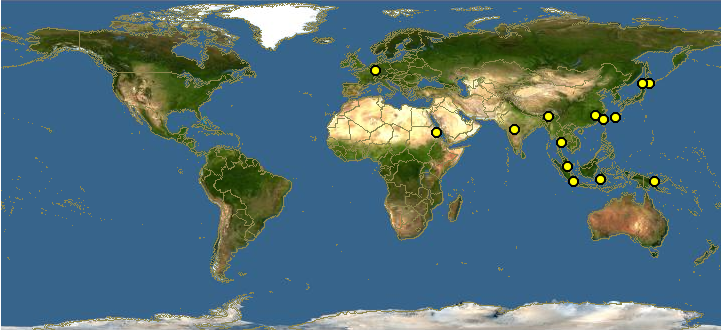 |
| Figure 12. Global distribution of Vespa affinis (Map from Discoverlife) |
2.3 Distribution across Singapore
Although Singapore is highly urbanized with pockets of green patches, the lesser banded hornet has been spotted in Singapore. The map below shows its distribution across Singapore. When in those areas, take a closer look and you may be in luck to spot one flying around!
| Googlemaps: Distribution of Vespa affinis across Singapore. (Biased towards ease of sampling) From: NUS Bee Lab |
(3) ECOLOGY
3.1 Perceived danger
Being most feared by humans, the lesser banded hornet is believed to be the most vicious and deadly. This could be due to the fact that nests are built on easily disturbed areas such as tree branches and bushes, making it easier for vibration to be transmitted (Lee, personal communication, 2015). Moreover, it might cause more damage as it has the largest colony sizes out of Singapore's three common hornet species (Lee, personal communication, 2015). However, it not especially defensive and will not attack unless the nest is disturbed. All hornets will attack in swarms when provoked to some extent. With moderately good vision, female workers can chase over long distances. Only females sting. Although the venom contains more pain-inducing components than other species, its venom may not be as potent as other bees and wasps (7)
3.1.1 Precautions
To prevent the possibility of getting stung or provoking these insects into attacking, precautionary measures are necessary (4,6):- Do not disturb or approach a nest
- Do not wear bright or flowery clothing
- Do not use scented cosmetic products
- Do not make sudden movement when encountering bees, wasps and hornet.
- Retreat as fast as possible. If not, lie facing down and cover head with arms or dive into a pool of water and stay submerged.
- If stung, seek medical attention immediately
- Never try to remove a nest by yourself.
- Contact any local pest management companies for inspection and treatment plan of the nest.
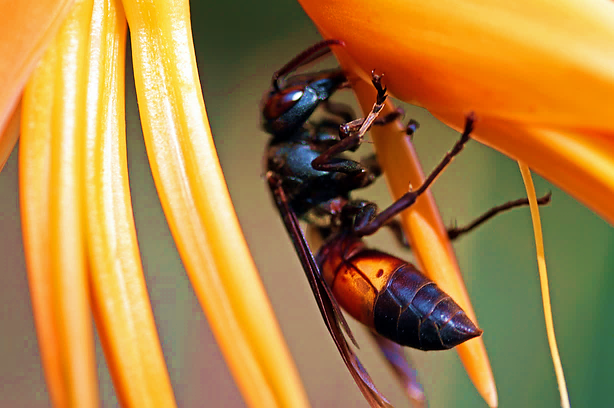
3.2 Pollination
Despite the lack of hairs on the body, the lesser banded hornet has the potential to pollinate flowers. Due to its ecological importance as a pollinator, the lesser banded hornet should only be removed if it poses a threat to humans. The following plants have been observed to be associated with this species (observation, 2015).
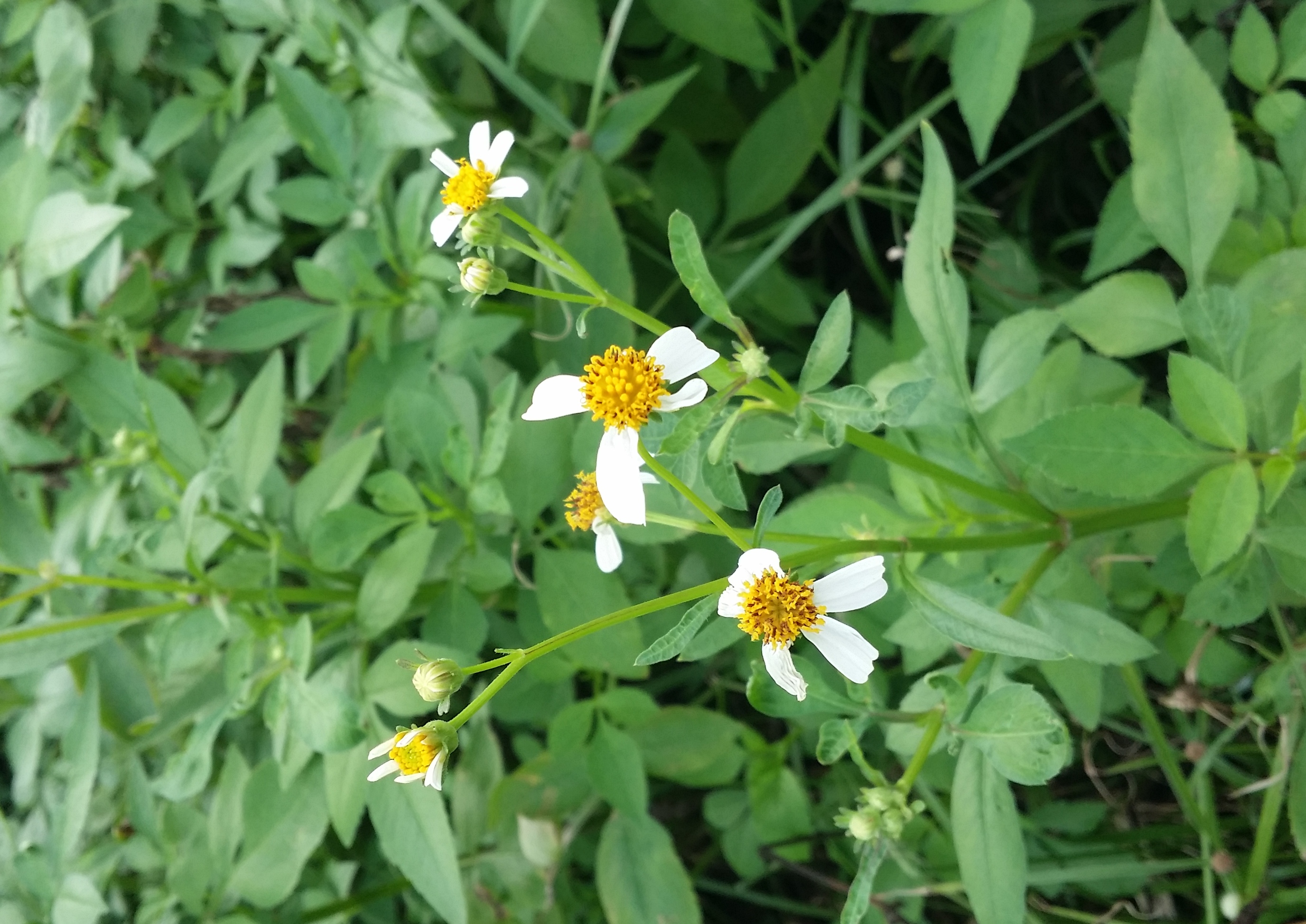 Figure 13. Bidens pilosa |
 Figure 14. Jatropha integerrima |
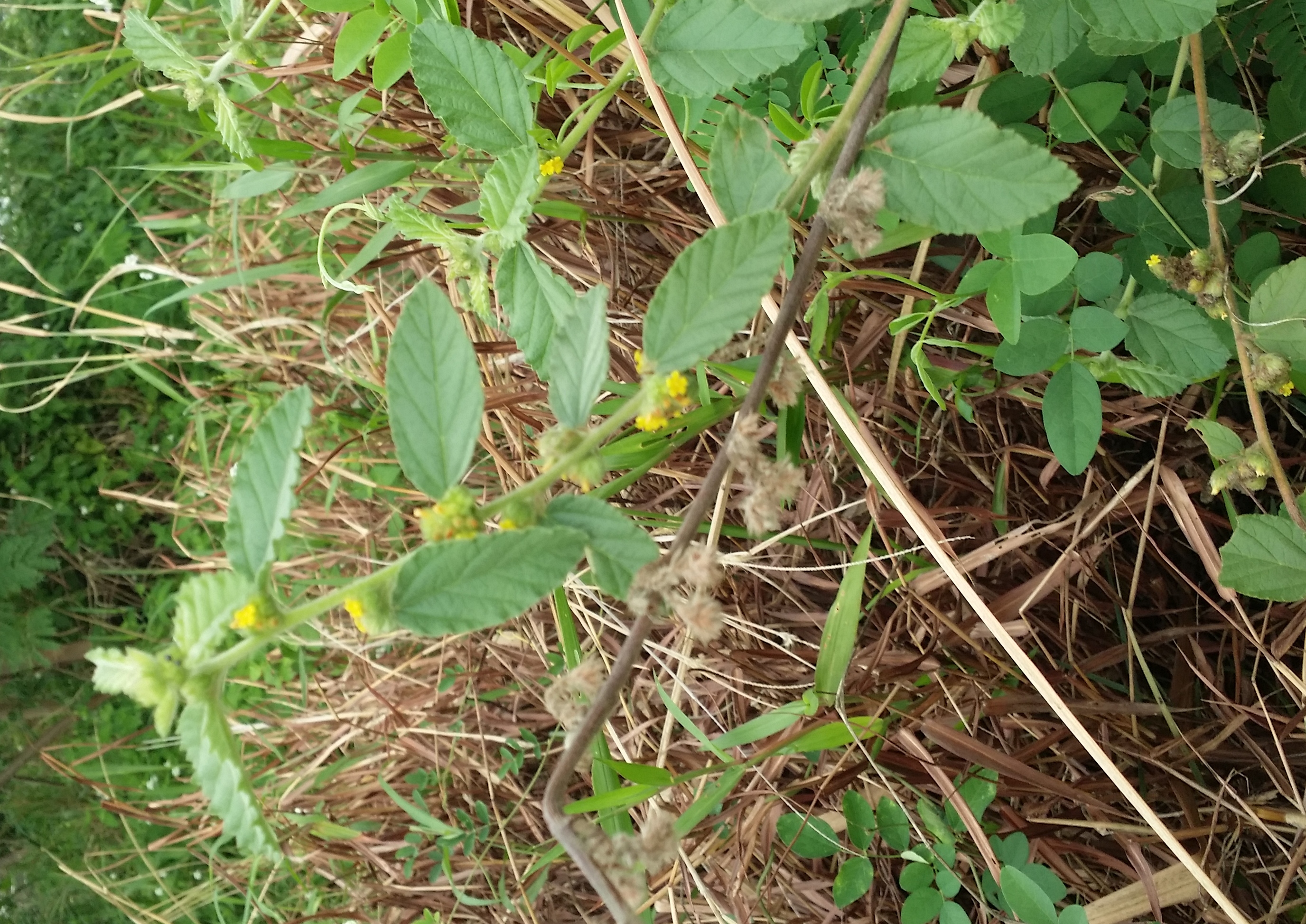 Figure 15. Waltheria indica |
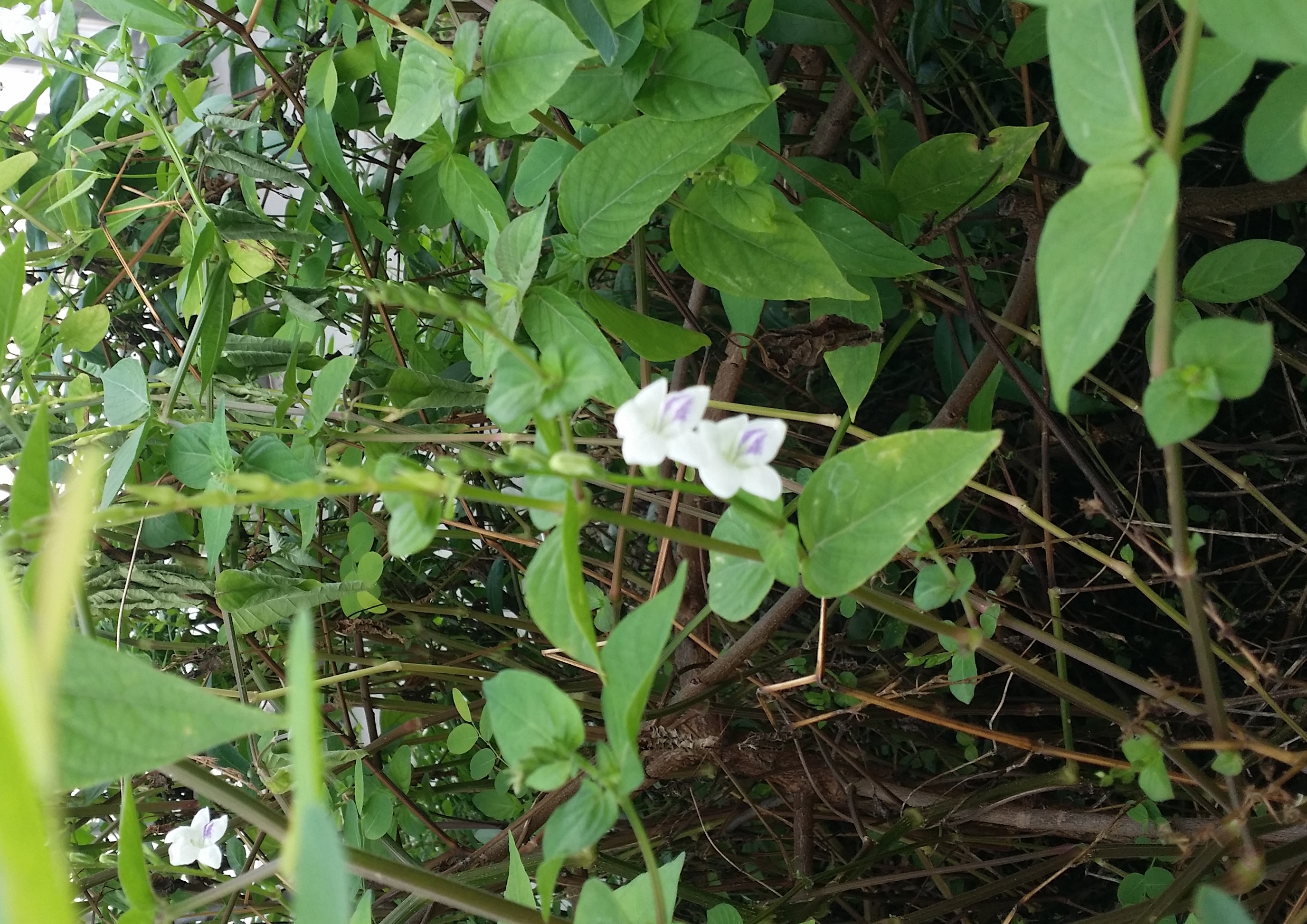 Figure 16. Asystasia gangetica ssp. micrantha |
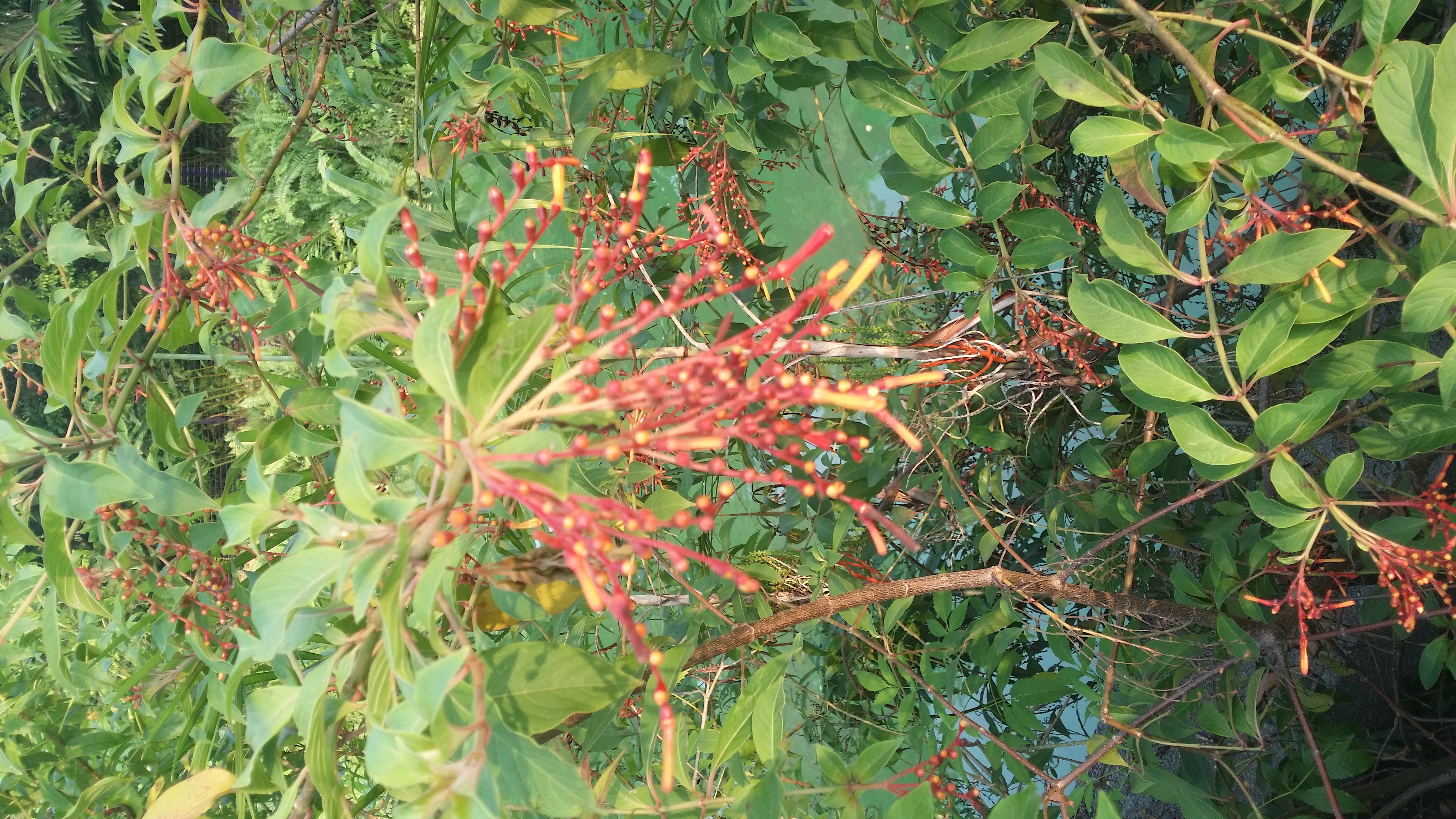 Figure 17. Hamelia patens |
Figure 18. Leea rubra |
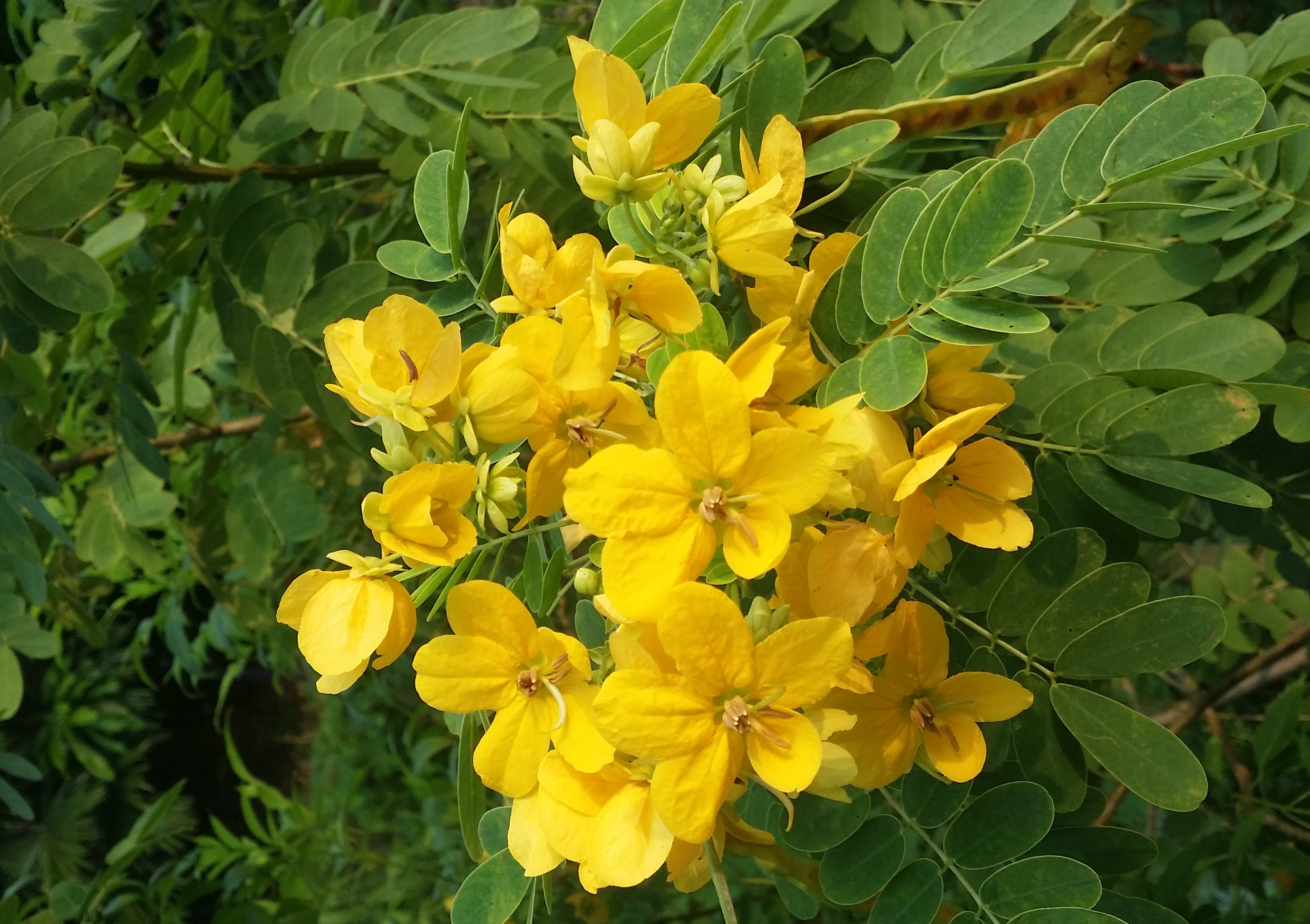 Figure 19. Senna surattensis |
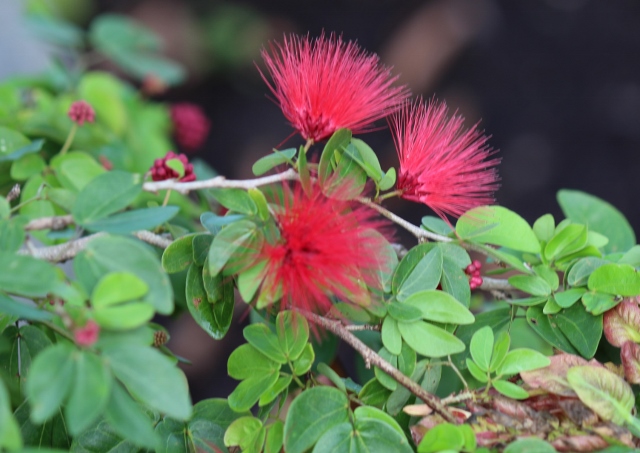 Figure 20. Calliandra tergemina var. emarginata |
| (Photos by Chua Muishan) |
|||
3.3 Conservation status
The lesser banded hornet has yet to be assessed by The IUCN Red List (IUCN) and more research has to be done on to assess the vulnerability of this species.
(4) DIET
4.1 Adult
With a highly versatile diet, the lesser banded hornet is a generalist that feeds on both carbohydrates (tree sap, nectar, fruits and larvae saliva) and proteinaceous food (carrion, Polistinae and Apis species) (2,11). Feeding on insects, the lesser banded hornet is a biological pest control. Their diet is mainly composed of liquefied foods.
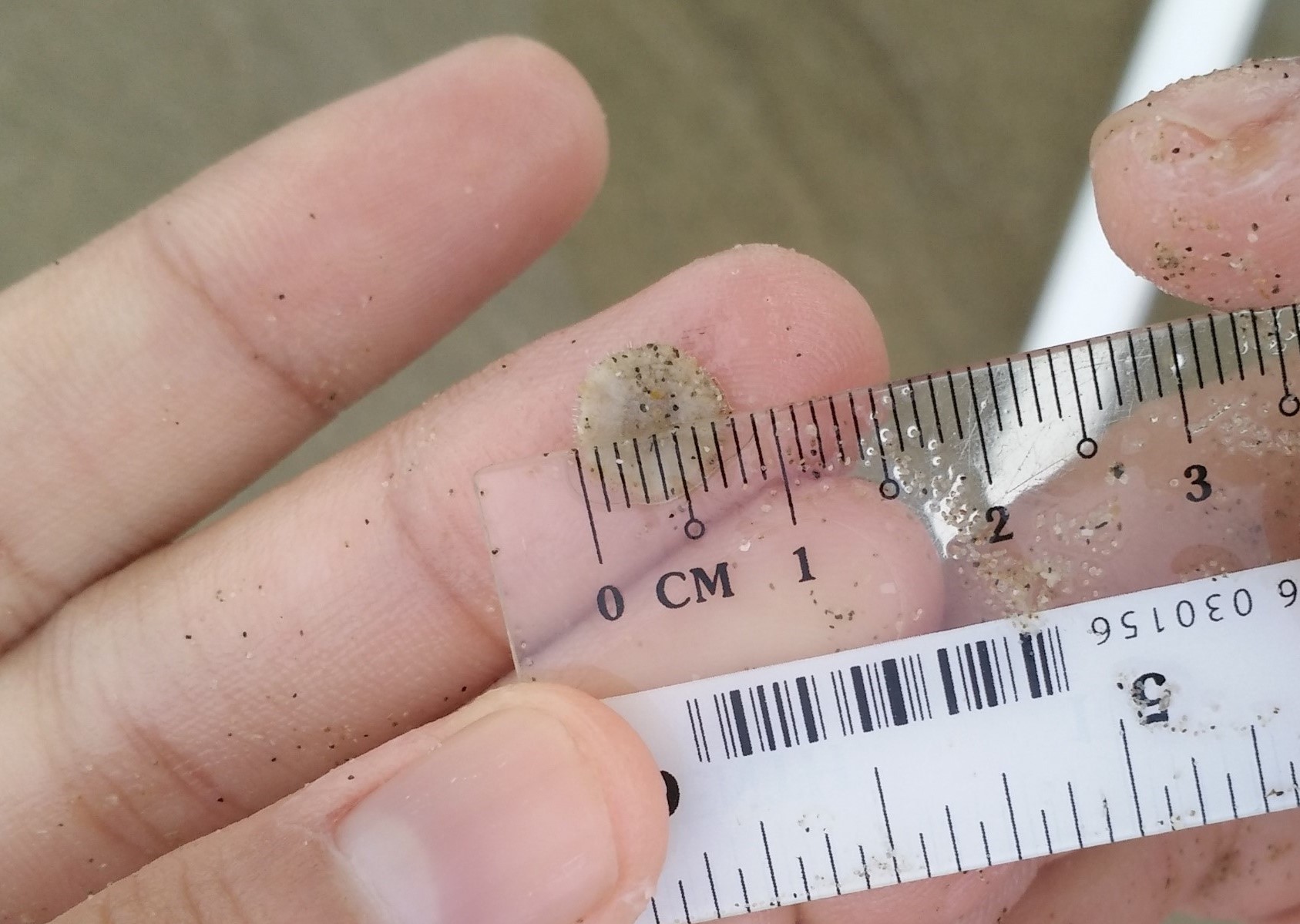 Figure 21. Vespa affinis feeding on nectar (Photo by Kwan Han) |
 Figure 22. Vespa affinis feeding on tree sap (Photo by Mark Eising) |
 Figure 23. Vespa affinis feeding on nectar (Photo by Joseph Wong) |
 Figure 24.Vespa affinis feeding on mussel (Photo by John X. Q. Lee) |
 Figure 25. Vespa affinis feeding on insect larvae (Photo by John X. Q. Lee) |
 Figure 26. Vespa affinis feeding on Apis cerana (Photo by John X. Q. Lee) |
4.2 Immature stages
Unlike adults, larvae only feed on proteinaceous food. Larvae feed on a pulp, which are pre-chewed by the female workers (7).
(5) BEHAVIOR
5.1 Life history
5.1.1 Life Cycle
Like all Hymenoptera, Vespa affinis undergoes complete metamorphosis - egg, larva, pupa and adult. In Japan, first workers emerge 34 days after nest initiation (8). In Singapore, first workers were recorded to emerge between 26 to 28 days after nest initiation, especially if more than one queen is involved (Lee, personal communication, 2015).
 Figure 27. Egg (Permission pending: Huang) |
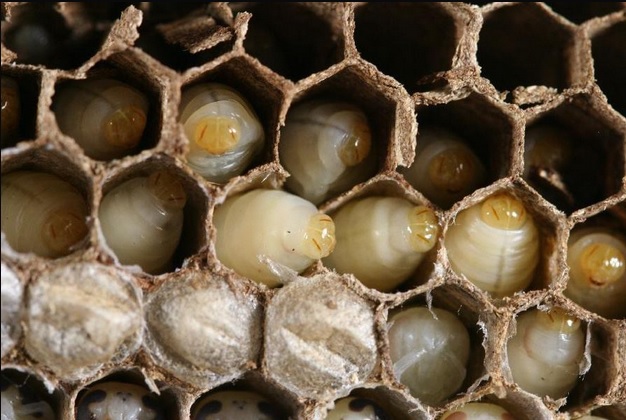 Figure 28. Larva (Permission pending: Huang) |
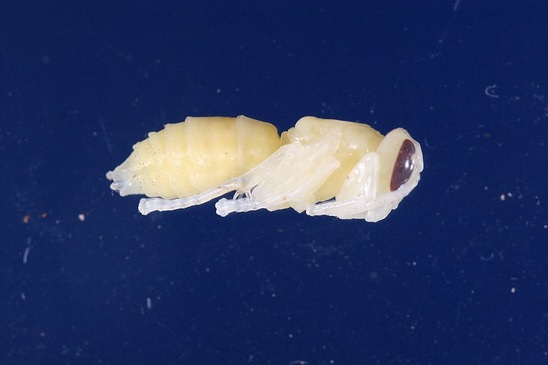 Figure 29. Pupa (Permission pending: Huang) |
5.1.2 Haplodiploidy
Haplodiploid sex determination is controlled by the queen - females usually develop from fertilized eggs (diploid) while males develop from unfertilized eggs and contain half the number of chromosome as females (haploid) (2,3). Through this reproductive division of labour, Vespa affinis has 3 caste - queen, male drones and female workers. As the queen and female workers differ morphologically, queens are reproductively viable while female workers are sterile (2,3). Male drones generally remain on the nest. Drones are short lived and only perform reproductive function towards the end of the colony cycle (2,3).
5.1.3 Colony Cycle
Vespa affinis has fairly long activity period and colony cycle. In sub-tropical regions like Hong Kong, queens appear from late March to early May and initiate new nests from April to May. These colonies usually last for 7 to 9 months (7). In Singapore, colonies are annual (1) and last for 10 to 11 months. These nests are initiated all year around and nests of different stages of development can be found at any given time throughout the year (Lee, personal communication, 2015).
5.2 Nesting Behavior
5.2.1 Eusociality
Vespa affinis is eusocial.Social wasps are characterized by cooperative care of young, overlap of generations within the society and reproductive division of labour (3). It establishes a well-determined hierarchy system of cast divisions where female workers are dominated by the queen. Similar to ants, Vespa species are known to cooperate to perform a collective task such as raiding of food sources (2). Although Vespa species are generally monogynous (Fig. 27), polygynous colonies (Fig. 28) have been recorded for Vespa affinis (10). More than 60% of nests in Singapore are polygynous with an average of three queens (Lee, personal communication, 2015).
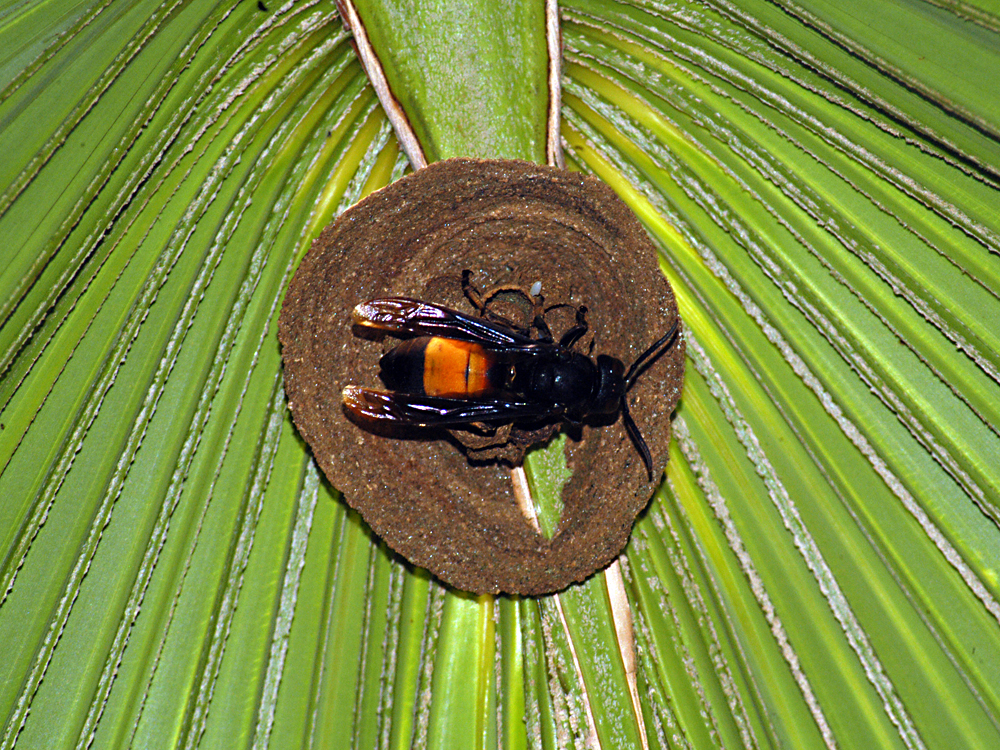 Figure 30. Embryo nest with one queen (Photo by John X. Q. Lee) |
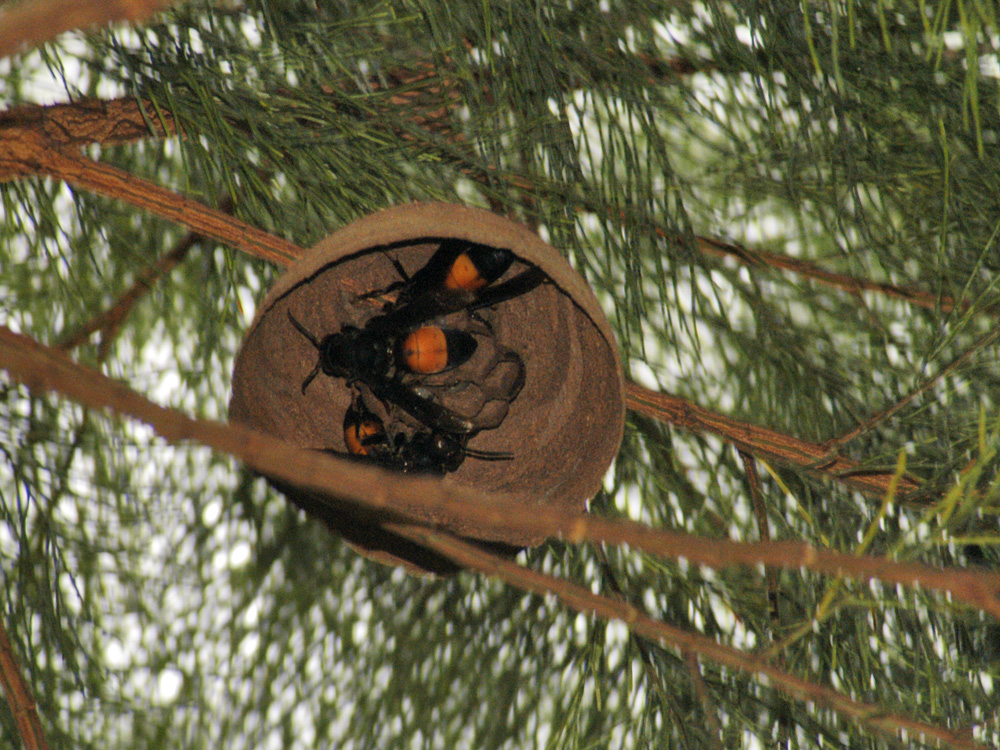 Figure 31. Embryo nest with multiple queens (Photo by John X. Q. Lee) |
5.2.2 Nest structure
Living in colonies, Vespa affinis constructs a paper nest which generally hangs from natural structures such as trees or shrubs (9). Nests in buildings are exposed, and are very seldom built in concealed crevices (8). The nest starts as a simple affair, where 4 – 6 cells were constructed at the tip of a stem. Small nests are shaped like a ball with a side entrance (Fig. 32) while larger nests are vertically elongated and may have multiple entrances (Fig. 33). The stacked multi-comb structure with a main central column is protected by a flask-shaped envelope (Fig. 34) (2). The combs were supported by short vertical pillars between adjacent combs (11).
 Figure 32. Small Vespa affinis nest (Photo by Tan KH) |
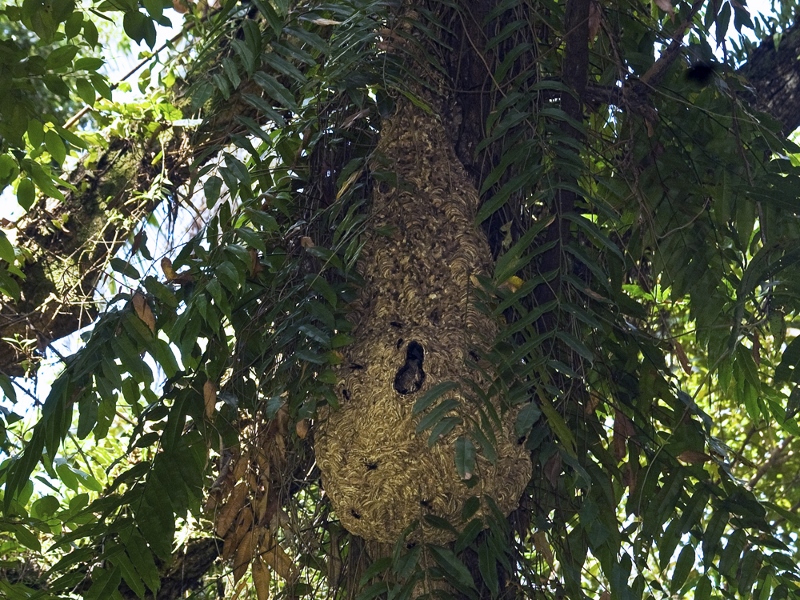 Figure 33. Large Vespa affinis nest (Photo by John X. Q. Lee) |
 Figure 34. Nest exterior of Vespa affinis (Photo by Vil) |
Figure 35. Nest interior of Vespa affinis (Permission pending: Huang) |
(6) MORPHOLOGY
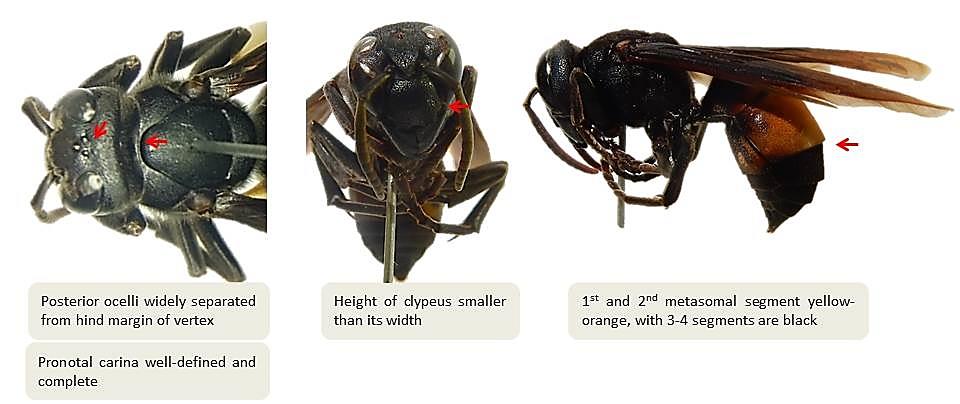
6.1 Vespa affinis
Figure 36. Identification of Vespa affinis (Photo by Chua Muishan) |
(7) Taxonomy and Systematics
7.1 Scientific classification
- Animalia
- Arthropoda
- Insecta
- Hymenoptera
- Vespoidea
- Vespidae Leach, 1815
- Vespa Linnaeus, 1758
- Vespa affinis (Linnaeus, 1764)
- Vespa Linnaeus, 1758
- Vespidae Leach, 1815
- Vespoidea
- Hymenoptera
- Insecta
- Arthropoda
Data from ITIS Catalogue of Lifeand Encyclopedia of Life
Eleven subspecies are currently recognized (1):
| Subspecies |
Informal Name |
| Vespa affinis affinis (Linnaeus, 1764) |
India and China |
| Vespa affinis alduini (Guérin-Méneville, 1831) |
Buru Island |
| Vespa affinis alticincta (van der Vecht, 1957) |
New Britian |
| Vespa affinis archiboldi (van der Vecht, 1957) |
Northern New Guinea |
| Vespa affinis continentalis (Bequard, 1936) |
Southern India |
| Vespa affinis hainensis (Bequard, 1936) |
Hainan Island |
| Vespa affinis indosinensis (Perkins, 1910) |
Indo-Malaya and Sumatra |
| Vespa affinis moluccana (van der Vecht, 1957) |
Ceram and Aru Islands |
| Vespa affinis nigriventris (van der Vecht, 1957) |
Palawan |
| Vespa affinis picea (Buysson, 1905) |
Southern New Guinea |
| Vespa affinis rufonigrans (van der Vecht, 1957) |
Borneo to Western New Guinea |
7.2 Phylogenetic relationships
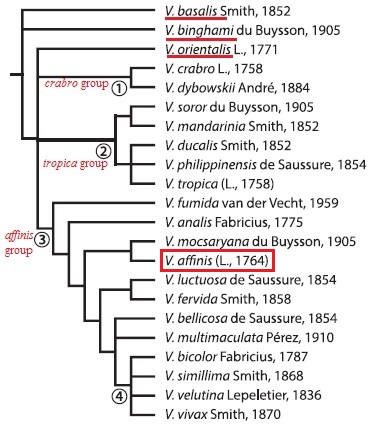
Using both morphological and/or molecular information as a basis for comparison, the phylogenetic relationships of Vespa species can be reconstructed.A prior phylogenetic analysis of the Vespa species has distinguished a main clade based on 11 morphological characters. However, the main clade has an unresolved basal node with four lineages – Vespa orientalis, crabro group, tropica group and affinis group (Fig. 37). Also, there are two species that remains unresolved at the base of the tree – Vespa binghami and Vespa basalis (Fig. 37) (10).
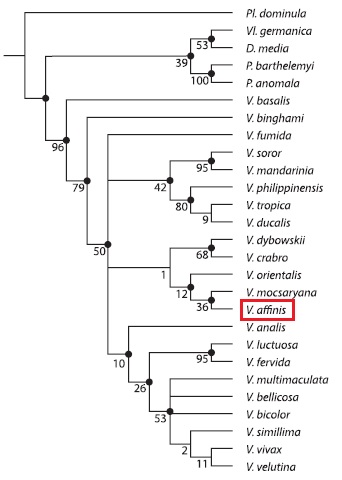
To improve prior analysis, both 45 morphological characters and molecular data from 4 mitochondrial and 2 nuclear genes were used for analysis (10). In the combined analysis tree, most clades of Vespa species are supported by morphological characters (denoted by the black nodes) while the four remaining clades are not diagnosed by morphological characters (Fig. 38). Both morphological and molecular characters are used to confirm the monophyly of the genus Vespa. Although the molecular data is incomplete, the addition of molecular data to the morphological matrix resulted in a stronger support of the tropica group. Also, by resolving the position of Vespa orientalis, the affinis group may not be monoplyletic, unlike prior analysis (10). Hence, to enhance the molecular data, specific primers could be used and the quality of DNA templates could be improved.
Click here to learn more about the morphological characters and markers used.
 |
 |
| Figure 37. Phylogeny of the genus Vespa after Archer based on 11 morphological characters (10). |
Figure 38. Support tree for the relationships with the genus Vespa based on a total evidence analysis (10). Black nodes are supported by morphological characters while no markings are diagnosed by molecular data only. Support for nodes are given in GC-values. |
7.3 Original description
Vespa affinis was first described by Linnaeus in 1764 as Apis affinis, where most bees described for the first time were simply classified under the genus Apis.
 |
| Figure 39. Screenshot of Vespa affinis as described in Systema naturae (Scanned document from Goettingen State and University Library) |
7.4 Type specimen
The type specimen is located in Uppsala University Museum of Evolution, Zoology section.

| Figure 40. Screenshot of Vespa affinis type specimen on the Catalogue of Type Specimen: Linnaean species. Uppsala University, Museum of Evolution. (12) |
7.5 Synonyms
Vespa formosana Sonan, 1927Data from Encyclopedia of Life
(8) CREDITS
8.1 Photo credits
Gopalakrishnakone – A Colour Guide to dangerous animalsHuang – Flickr
Kwan Han – Nature Love You
John S. Ascher – Discover Life
John X . Q Lee – Vespa-bicolour
Joseph Wong – Flickr
Mark Eising - Markeisingbirding
Nikita Hengbok – Flickr
Sasithron – Flickr
Tan KH – Singapore Wild Animals
Troup Dresser – Flickr
Vil Sandi – Flickr
8.2 References
1. Archer, M. E. (1997). Taxonomy, distribution and nesting biology of Vespa affinis (L.) and Vespa mocsaryana du Buysson (Hym., Vespinae). Entomologist's Monthly Magazine (United Kingdom).2. Barthélémy, C. (2008). Provisional Guide to the Social Vespids of HongKong (Hymenoptera: Vespidae).3. Bourke, A. F. (1988). Worker reproduction in the higher eusocial Hymenoptera. Quarterly Review of Biology, 291-311.
4. Gopalakrishnakone, P. (1990). A colour guide to dangerous animals. NUS Press.
5. Lee, H. L., Krishnasamy, M., & Jeffery, J. (2005). A fatal case of anaphylactic shock caused by the lesser banded hornet, Vespa affinis indosinensis in peninsular Malaysia. Tropical biomedicine, 22(1), 81-82.
6. Lee, J. X. Q. (2012). A Field Guide to the Bees & Wasps of Singapore. Singapore: NSS Pocket Guide Series
7. Lee, J. X. Q. (2009). Potentially Dangerous Bees and Wasps of Hong Kong. Hong Kong: Hong Kong Entomological Society.
8. Linnaeus, C. (1758). Systema Naturæ per Regna Tria Naturæ, Secundum Classes, Ordines, Genera, Species, cum Characteribus, Differentiis. Synonymis, Locis. Tomus. Holmiæ [Stockholm] (Sweden): Impensis Direct. Laurentii Salvii, 1(10)
9. Martin, S. J. (1992). Development of the embryo nest of Vespa affinis (Hymenoptera: Vespidae) in southern Japan. Insectes Sociaux, 39(1), 45-57.
10. Perrard, A., Pickett, K., Villemant, C., Kojima, J. I., & Carpenter, J. (2013). Phylogeny of hornets: a total evidence approach (Hymenoptera, Vespidae, Vespinae, Vespa). Journal of Hymenoptera Research, 32, 1-15.
11. Ross, K. G., & Matthews, R. W. (Eds.). (1991). The social biology of wasps. Cornell University Press.
12. Wallin L. (2001). Catalogue of type specimens. 4. Linnaean specimens. 6th ed. [ebook] Uppsala, Sweden: Uppsala University, p.20. Available at: http://www.evolutionsmuseet.uu.se/samling/UUZM04_Linnaeus.pdf [Accessed 10 November 2015].

